Star Principle
Richard Koch (building on BCG’s Growth–Share “Star”)
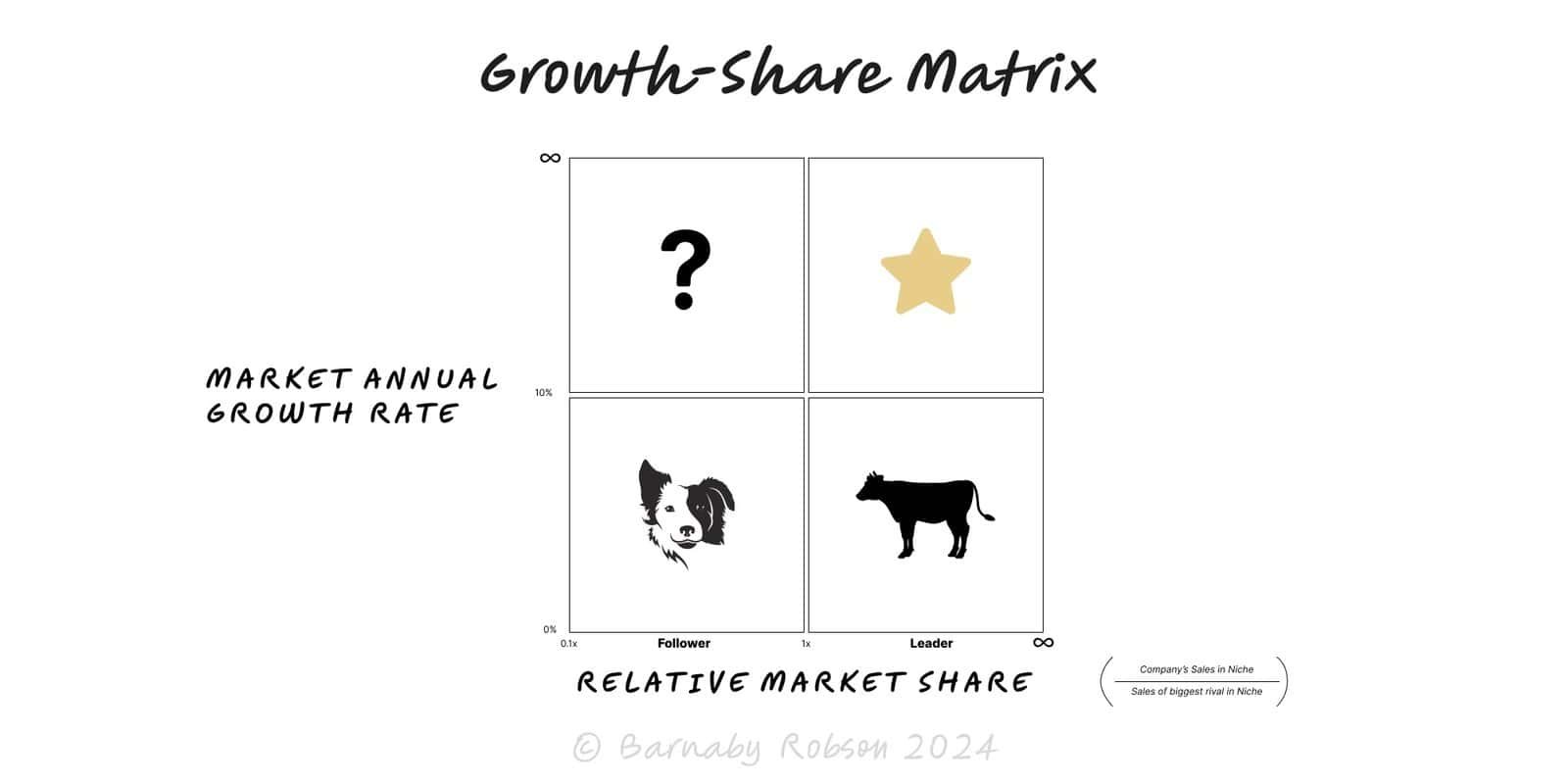
Koch’s Star Principle says the best businesses to build or back are category leaders in rapidly growing markets. Growth lifts the whole niche; leadership captures the bulk of the economics through scale, brand, data and network effects. Rather than diversify, double down on the winning niche and compound advantage.
I wrote. a separate article on using the Star Principle here: https://barnabyrobson.org/the-star-principle-better-investment-decisions
Definition – a Star = clear market leader (share, mindshare, or network density) in a fast-growing niche.
Compounding – growth expands the pie while leadership improves unit economics (lower CAC, higher WTP, better retention).
Focus beats breadth – concentrating resources on the lead product/segment increases moat depth.
Category design – tighten the niche until you are No.1; name and frame the category so comparisons favour you.
Moat flywheels – scale, brand, data, and partner ecosystems reinforce leadership as volume rises.
Founders – pick or niche-down to a segment you can lead; avoid “average in a big market.”
Investors – screen for founder-led category leaders with fast category growth and improving unit economics.
Corporate strategy – portfolio pruning to concentrate on star businesses; spin out or sell non-stars.
Define the niche crisply – job-to-be-done, target customer, channel, geography; tighten until leadership is demonstrable.
Verify growth – double-digit YoY demand (revenue/search/installs) with room to run; avoid faddish spikes.
Prove leadership – market share, share of voice, network density, or switching costs; show gaps vs No.2.
Focus resources – allocate talent, capex and marketing to the core star; deprioritise side quests.
Deepen isolating mechanisms – strengthen distribution, community, data assets, standards, and complements.
Widen the lead – expand adjacently (features/segments/geos) only where it reinforces the core dominance.
Instrument – track category growth, your relative share, CAC payback, retention, and advantage half-life.
Govern capital – reinvest free cash where it increases leadership; avoid diworsification.
Vague “leadership” – vanity metrics or fuzzy categories; define the market so an independent auditor would agree you’re No.1.
Growth mirages – temporary hype or subsidised demand; require durable pull and improving unit economics.
Core neglect – chasing adjacencies too early erodes focus and moat.
Platform dependency – if distribution is rented (app store/SEO), your “lead” can vanish with a policy tweak; diversify channels.
Complacency – stars age; monitor when growth slows and refresh the category or create the next niche.
